Traveler’s diarrhea can affect 30 to 70% of travelers. While the discomfort is over in just a few days for most, some travelers develop more serious conditions. Either way, it’s largely inconvenient, especially on a vacation you’ve been looking forward to. Let’s talk about how you can deal with traveler’s diarrhea.
What Causes Traveler’s Diarrhea
Traveler’s Diarrhea (TD) is commonly caused by ingesting bacteria, viruses, or protozoa transmitted via the fecal-oral route – this is when you consume food or water contaminated with infected fecal particles, or by touching your mouth with dirty or improperly washed hands.
You can catch acute gastrointestinal illnesses anywhere in the world but it’s called traveler’s diarrhea as it’s often contracted while visiting places where food hygiene practices are not always held to a high standard. Limited sanitation infrastructure can also increase the risks.
It’s important to be vigilant about how your food is prepared and where your drinking water comes from.
How to Deal With Traveler’s Diarrhea
The top three recommendations for managing traveler’s diarrhea are increasing fluid intake, anti-motility agents, and antibiotics for severe cases. However, it’s important to know when and how to use these strategies.
Let’s discuss our top 7 tips for dealing with traveler’s diarrhea.
Identify the severity of your Traveler’s Diarrhea
Traveler’s Diarrhea can be categorized as either mild, moderate, or severe depending on the symptoms.
Mild TD is characterized by a few unformed stools but is generally tolerable and does not interfere with daily activities. Moderate TD is more distressing as it interferes with daily activities and presents with loose or liquid stools, possibly accompanied by cramps or nausea.
In more severe cases, it becomes debilitating. In addition to the previously mentioned symptoms, one may see blood in their stool. Cramps and nausea also occur in severe cases and may also co-occur with chills, severe thirst, or inability to keep liquids down.
Prevent dehydration
Your top priority when managing traveler’s diarrhea is to prevent dehydration. Increasing your fluid intake should be the first thing you do when you notice the first signs of diarrhea – generally defined as more than three episodes of unformed stools within 24 hours.
Most cases of Traveler’s Diarrhea don’t cause significant dehydration in healthy adults but some travelers are at increased risk of severe diarrhea and dehydration. These include young children, older adults, individuals with low stomach acid, inflammatory bowel disease (IBS), and those who take medication for high blood pressure.
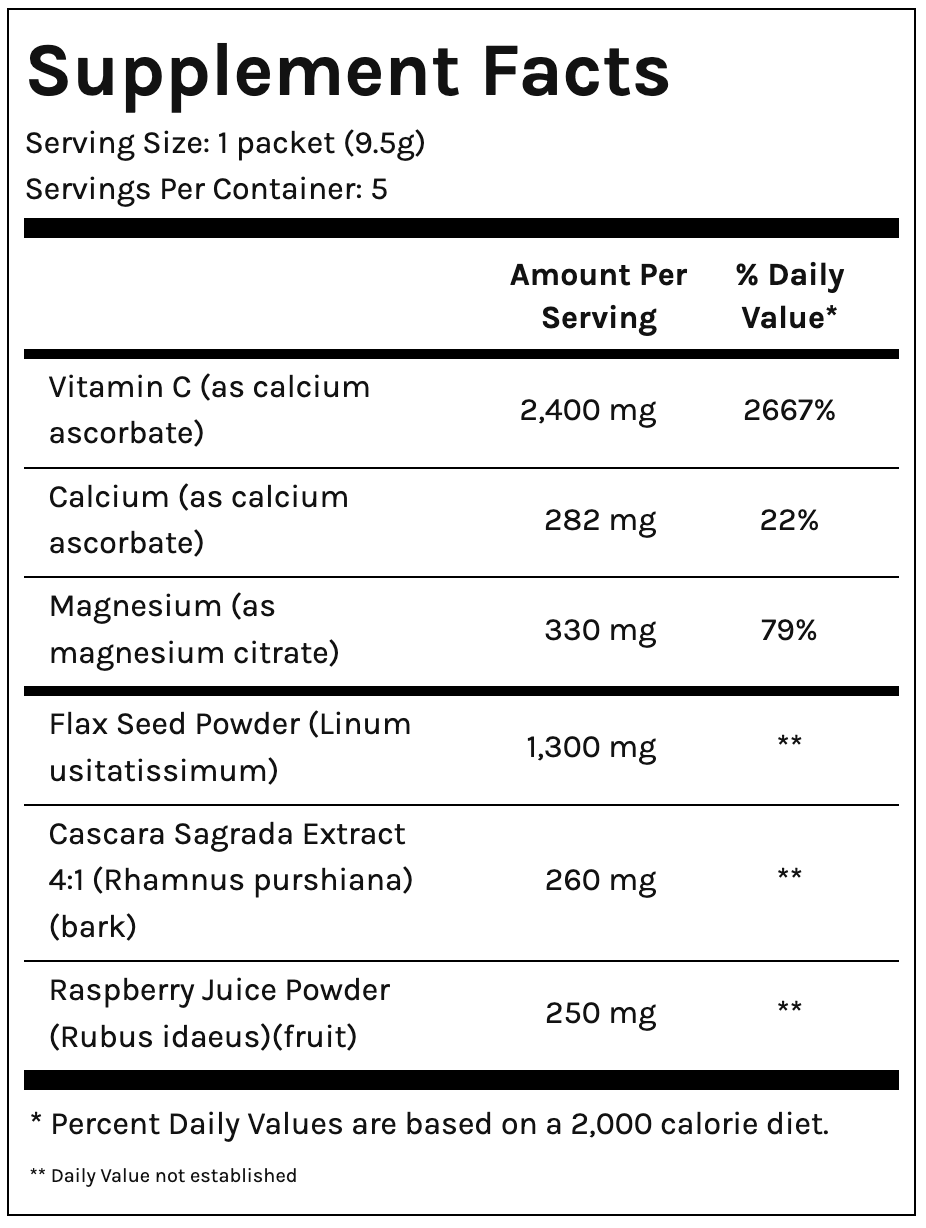
Oral rehydration solutions (ORS), a mixture of salt and sugar designed to be rapidly absorbed by your intestinal tract, can be purchased from pharmacies as quick remedies for dehydration. Magnesium citrate can also help absorb water into your intestinal tract while also bulking up your stools.
Regulate your intestinal contractions
Anti-motility agents are often prescribed for mild to moderate diarrhea. Drugs like Loperamide and Pepto-Bismol alleviate the symptoms of diarrhea but they also have side effects so it’s important to discuss with your doctor prior.
Loperamide may cause cardiac events when exceeding the recommended amount or taken with other medications such as quinine, ritonavir, erythromycin, and others. It is not recommended for children under 6 Pepto-Bismol on the other hand can cause constipation and is not recommended for children under 12 and pregnant women.
So what’s a safe and natural way to regulate your intestinal tract’s contractions? Buffered Vitamin C, or “gentler” forms of Vitamin C that are better tolerated by the gut, can promote proper muscle relaxation and contraction.
Use antibiotics with caution
Antibiotics can be used for moderate to severe diarrhea. These cases usually have a high risk for diarrhea-related complications. Consider packing emergency antibiotics in case Traveler’s Diarrhea starts to get in the way of your planned activities.
The safest way to go about it is to consult with your doctor or a travel health specialist. They will educate you on how to identify the severity of your TD and which antibiotics should be used. You should keep in mind that some strains of bacteria that cause traveler’s diarrhea are antibiotic-resistant. Do research on the prevalent strains in your destination before leaving.
Consider bulking agents for managing traveler’s diarrhea
Sometimes bulking agents such as psyllium can help control liquid or unformed stools. Bulking agents in the form of fibers can help increase fecal mass and prevent runny bowel movements. They can also help regulate the contractions of your digestive system in small amounts.
Try consuming fiber-rich foods or supplements to help form your stools and control your bowel movement.
Eat easily digestible foods
While most would advise against eating since diarrhea can affect the absorption of nutrients, you should not do away with food entirely. It would be helpful to eat easy-to-digest foods. The BRAT diet is often recommended for diarrhea: bananas, rice, apple sauce, and toast.
Know when to seek medical attention
If self-treatment does not resolve the problem, seek medical attention. Signs of dehydration include excessive thirst, dark-colored urine, infrequent urination, drowsiness, dizziness, or nausea. You should also seek professional medical attention when taking an antibiotic does not resolve symptoms of severe Traveler’s Diarrhea.
Preventing Traveler’s Diarrhea
Prevention is always better than cure. Make sure to take precautions against Traveler’s Diarrhea by eating only hot or pre-packaged foods, drinking bottled or thoroughly filtered and purified water, and avoiding high-risk foods such as raw fruits and vegetables.
You can also prevent bowel problems from disrupting your travel plans by protecting your gut health. A natural supplement that supports bowel regularity, improves stool consistency, improves digestive function, and provides immunity support can help you fight against gastrointestinal issues. Travel-Eeze does all that and more in single-serving packets that travel with you.